OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus 2023 PDF Download: Candidates Are you preparing for OSSC Assistant Curator Exam 2023 Then this article is for You……….! Here The OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus 2023 And Exam Pattern is available in detail. So the Candidates, who applied for OSSC Assistant Curator Jobs 2023 and Searching Online for OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus 2023, will get complete information here. The Odisha Staff Selection Commission recently announced the OSSC Assistant Curator Exam 2023. So the Applicants who applied for OSSC Assistant Curator Exam must check this article. The OSSC Assistant Curator Exam is quite tough to be Qualified and there will be a huge competition for the Examination. So the Contenders should practice Hard. So, to help those candidates we are here with the Updated OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus and Exam Structure.
OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus 2023 PDF
| Organization | Odisha Staff Selection Commission (OSSC) |
| Posts | Assistant Curator |
| Category | Syllabus |
| Job Location | Odisha |
| Official Website | ossc.gov.in |
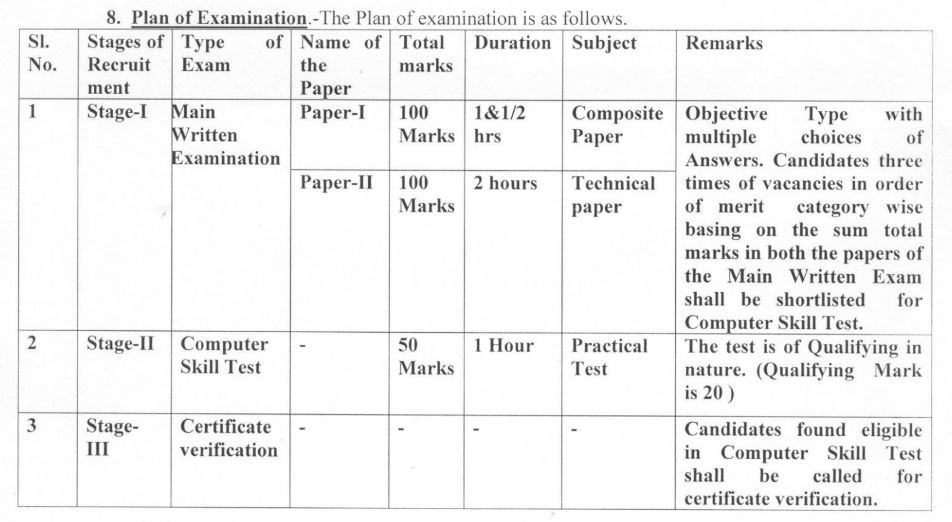
OSSC Assistant Curator Exam Pattern 2023
Download OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus & Exam Pattern PDF 2023
Download OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus & Exam Pattern 2023 PDF Here: The Candidates who have been searching for the OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus can get a complete Syllabus from this article……….So the candidates who have applied for the OSSC Assistant Curator 2023 and preparing for the OSSC Assistant Curator Prelims and Mains Exam 2023 are advised to take a look at this page now. Here the OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus & Exam Pattern are available in detail.
Syllabus Of Technical Paper For The Post Of Assistant Curator: –
- COLLECTION MANAGEMENT
- Acquisition:
– History of collection.
– Ethics of collection
– Modes of acquisition: Gift / bequeath, excavation, exploration, expedition, loan exchange, purchase, confiscation and fabrication.
– Art purchase committee
– Insurance
– Replication/duplication, forgery, export/import, auction.
- Registration & Documentation:
– Accessioning & deaccessioning.
– Numbering
– Marking
– Identification, classification, dating, search of bibliographical reference.
– Cataloguing.
– Indexing
– Photo documentation.
– Computerized documentation, digital cataloguing.
– Problems in documentation, e.g., fabricated exhibits, plastic art, oral historynonmaterial culture / intangible heritage), etc.
• Storage & transport of collection.
• Packaging material, methods, etc.
• Transhipment – modes, methods, insurance.
2. PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Strategic planning: resources, core competence, comparative advantage, USP, etc. Feasibility study.
Setting goal (target).
• Resource mobilization fund, space, know-how/expertise, collection etc. Selection & organization of project team.
• Project execution/implementation.
• Evaluation/impact factors/assessment, correction/ adjustment. Project report.Business and operational management.
Organizational Theory.Museology & entrepreneurship.
- EXHIBITION & EDUCATION
Display & Exhibition
– Purpose and principles.
– Display furniture and fixtures: cases, pedestals, stands, panels, mounts, structures, etc.
– Lighting fixtures.
– Circulation: random, suggestive, directional.
-Labels: types, material, size, language, position, execution, evaluation, etc.; digital label
– Visual & verbal aids; charts, graphs /graphics, photographs, film/video, CD-ROM/ DVD, etc.
– Types of exhibits: original/ fabricated, static/ movable, models (scale/ non-scale, working/non-working), participatory/ interactive, diorama/ habitat group, tableaux,
etc.
– Types of exhibitions: object-oriented/concept-oriented, thematic, contextual, Chronological, geographical, integral, comparative, natural, synthetic, didactic, Special, permanent/temporary/traveling/circulating/mobile, etc.
Exhibition Designing
– Principles of exhibition designing.
– Human factors: basic human dimensions (anthropomorphic data), ergonomics, human nature & tendencies.
– Principles of exhibit arrangement & use of space.
– Objective (individual exhibits & overall exhibition).
– Conceptualisation, goal/target, theme development, sequencing & story development, reference research.
– Curator-Designer- Educator interaction; division of labour.
– Planning & designing exhibits in a particular setting: layout drawing, mock-up (scale model), colour scheme, accessibility, visitor circulation, evaluation (front-end) & correction.
– Designing individual exhibits, working sheets/ drawings, collection/ fabrication and arrangement/mounting/installation.
– Animation techniques: optical, mechanical, electrical, electromechanical, electronic, computerized, robotics, Polaroid, etc.
– Interaction/ participation modes.
– Virtual reality, augmented reality, immersive visualization.
– Principles of exhibit lighting.
– Audio-visual aids. – Text: content, size, fonts, background, placement, and storyline. – Documentation. – Scheduling.
– Evaluation: front-end, formative & summative, correction.
- Principles & problems of organizing exhibitions in different museum set-up:
Art, History, Archaeology, Anthropology, Ethnic Art, Zoology, Botany, Geology, Geography, Marine Science, Fishery, Forestry, Biography/ Personalia, Literary, Philatelic, Science & Technology, etc.
Syllabus Of Technical Paper For The Post Of Assistant Conservator:
• Care & Conservation
– Understanding conservation, preservation & restoration. – Ethics of conservation.
– Material composition of objects & their properties, introduction to basic chemistry.
– Laboratory documentation procedures, Photo documentation.
– Instruments & equipment used in a conservation laboratory: Principles & uses
• Museum environment: Humidity, temperature, light and their effects individual &
combined) on cultural objects.
- Atmospheric pollution & their effect on cultural properties.
- Monitoring of museum environment, control & remedial measures
Various agents/factors for deterioration of cultural objects: Physical, chemical & biological; control & remedy.
• Deterioration, conservation & care of organic materials:
– Wood, bamboo, basketry, reed, palm-leaf, birch-bark, etc. Leather, parchment, vellum, hair, feather, etc.
Paper, papyrus prints, drawings, manuscripts, photographs, etc. Textiles.
– Ivory, bone, horn & antler.
Natural history specimens.
Deterioration, conservation & care of inorganic and siliceous materials:
– Metals: iron & steel, copper, gold, silver, lead, tin and their alloys, pewter.
– Clay & terracotta, porcelain, glass, faience, enamel.
Stone.
Geological specimens
– minerals, rocks & fossils.
– Polymer, audio/video tapes, CD / DVDs.
• Deterioration, conservation & care of composite materials:
– Easel painting – Ethnographical objects, scientific instruments, etc.
– Building, monuments, murals, etc.
• Museum architecture & climate control.
• Museum store & storage of cultural properties store design, climate control, and objects
storage from the point of view of conservation.
• Packaging, transport & exhibition: safety of the objects in transit & in display Recent
advancements in conservation.
• Museum & research:
– Research methodology (principles).
Research collection/collection management.
Research on exhibition – Research on education and other programs. – Research on environment and conservation. – Research on visitors.
• Quality management:
– Concepts, standards, ethics. – Goal setting
Quality tools – Evaluation – Identification of non-conformance. – Correction – Social audit in museums.
Syllabus Of Technical Paper For The Post Of Research Assistant
PAPER-I (COMPULSORY)
UNIT-1
Concept of Social Development & Development Research: Types of Society (Egalitarian, Segmental. Feudal and Capitalistic) and their development: Barriers and stimulants in social development: Role of Technology in social development. Human Development Index (HDI). Globalization and its impact on socio-cultural dimensions, Indigenous Recourse Management, Social Impact Assessment (SIA). Development and Rehabilitation Induced Displacement, Factors of Migration and its consequences.
UNIT- II
Demography with reference to ST Populations of India: Age – Sex composition. Sex ratio, Fertility, Fecundity, Mortality, Morbidity, Nuptiality, Migration. Life Expectancy. Literacy. Work Party Participation. Dependency Ratio Population Growth Rates. Infant Mortality Rate. Worker Classification. Labour Force Participation and Decline of Indigenous population in India.
UNIT – III
Techniques in Social Research: Research Design. Qualitative Vs Quantitative studies. Sampling: probability and non-probability sampling, sample design, sample size. Controlled group vs Experimental group. Covert vrs Overt study. Hypothesis: Inductive and Deductive. Logic of testing hypothesis. Questionnaire, Schedule. Observation, Interview, Case Study. Life History. Cross-cultural, PRA, RRA. Focused Group Discussion (FGD). Index Number, Quantity and Price Indices. Consumer Price Index (CPI) & Wholesale Price Index (WPI), Ranking Methods and its Application and Scaling Techniques.
UNIT-IVElementary Statistics in Social Research: Collection, compilation, and presentation of data charts & diagrams. Frequency distribution, measures of central tendency, measures of dispersion, moments, skewness & kurtosis. Curve fitting by the method of least squares, simple correlation and regression. Classical and axiomatic definitions of probability, theorems of total and compound probability. Random variable and mathematical expectation. Binomial, Poisson, Normal, x, t, F, 2, distributions, their properties and uses, tests of significance based on these distributions. Components of time series, trend fitting by moving averages, and least squares method, Sampling Techniques: Sampling vrs Census, Sampling and non-sampling errors, simple random sampling.
UNIT-V
Ethics in Social Science Research: The value of research and research ethics. Obligations to society. Obligations to subjects. Informed Consent. Intellectual Property Right, Pattern right. Copyright, Plagiarism, Ethics committees and IRB’s.
UNIT-VI
Knowledge of Computer Application in Social Sciences: Components of Computer and its Classification, Hardware and Software. Knowledge on Word Processor. Spread Sheet and Electronic Presentation Package. Basic Idea about MS Office and proficiency for its use. Basics of Internet. Uses of Internet, data relating to Social Science. Managing an email account, use of different software for processing and analysis of cases relating to Social Science.
Syllabus Of Technical Paper For The Post Of Research Assistant
(Candidate to choose one of subjects listed below)
PAPER-II – OPTIONAL APPLIED ECONOMICS
UNIT-I
Economic Growth and Development: Factors affecting economic growth, Concepts of GDP and National Income, Poverty and Inequality, Human Development Indicators-HDI.
Economic Growth In India and Sectoral Composition – Impacts of liberalization role of FDI.
Investments Criteria in Developing countries, Alternative Investments Criteria and Cost – Benefit Analysis, Project Evaluation
Budget- Kinds of Budget: Traditional Budgeting Program-Budget. Zero Base Budget. Outcome Budgeting and Gender Budget, Deficit Financing and Economic Development.
UNIT- II
Banking and Nonbanking Finance in India: Role of RBI and SEBI.
Financial Inclusion: Concept, Need and trend in India: strategy to extend financial services, Institutional changes required for financial inclusion, Role of savings and rural credit structure, Micro Finance and role of SHGs. Importance of Rural Credit: Agencies for Rural Credit – Formal and Informal; Small Farmers Development Agency, National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development, Rangarajan Committee on Financial system.
UNIT-III
Role of Education and Health in economic development: Demand and supply of education and their determinants, Cost and benefits of education, Manpower planning: programming and input-output models, Educational finance and need for privatization with special reference to India.
Determinants of Health, Economic dimensions of health care demand and supply of health care, financing of health care, Issues in health care delivery, Inequalities in health care: Income, class and gender dimensions, Public-Private Partnership.
Economic Development and Environment, Poverty and Environment, Climate change – Problems, impacts and policy.
Pricing in social sector and issues of subsidies with special reference to India.
UNIT – IV
Role of fiscal and monetary policy in economic development and need for coordination: Indian Tax system: revenues of the centre, State and Local bodies, major taxes in India: Direct and Indirect, Recent Tax Reforms, need for GST, Non tax revenues of Centre, State and Local bodies.
Public expenditure in India-trends and composition, Globalization, WTO and their impacts on Indian Economy, Issues of privatization and safety nets in Indian economy.
Fiscal federalism in India, Center-state financial relations, Horizontal and vertical imbalances, Resource Transfer and role of Finance Commission and Niti Aayog, Criteria of Transfer and impacts, Problems of state finances and indebtedness, FRBM Act 2003 and fiscal reforms, Decentralized governance and local level finances.
UNIT – V
Agriculture in economic development: Production function approach and estimation methods, Land reforms in India, Technological changes and impacts, pricing of agricultural Inputs and outputs, agricultural finance and subsidies, marketing and warehousing. Role of public investment and capital formation in agriculture. Issues of Food security and role of PDS, resource uses and policies for sustainable agriculture. Crop Insurance in India.
Growth and pattern of Industrialization in India, Evolution of Industrial policies, problems of sickness, privatization and disinvestment debate, role of MSME sector, employment generation and labour market reforms.
UNIT- VI
Odisha Economy: Growth and Structure- Sectoral composition and trends, Poverty IssuesSocial and Regional dimensions, Regional Imbalances in development, Rural development Issues in Odisha
Social sector development in Odisha: health and education scenario – Problems and prospects.
Agriculture in Odisha: cropping pattern and diversity in agriculture, Institutional issues and role of technology. Problems and prospects.
Industrialization in Odisha: trends and achievements, Issues, problems and prospects. Role of MSME sector.
State Finances: trends and issues. problems of resource mobilization and prospects. Decentralization and local level finances in Odisha.
Paper-II -OPTIONAL SOCIAL WORK
UNIT-I
Basic Concepts: Social Work, Social Service, Social Welfare. Social Security, Social Reform Social Change, Social Justice, Human Rights, Social Development, Social Exclusion. Definition and scope. Social Work Ethics: Philosophical base of Social Work, Ethical Values in Special Work
UNIT- II
Social Work Methods: Social Case Work, Social Group Work, Community Organization, Social Action.
Social Movement (Bhoodan, Chipo), Ethnic Sensitive Social Work Practice (ESP).
UNIT- III
Social Problems: Concept and meaning, Major social problems in India (Poverty, Castes, Population). The response of Social Work, Social Legislation and Social Policy (Concepts Objections and needs).
UNIT – IV
Social Work Practice in Rural and Urban Communities: Concept of Rural and Urban Development. Issues faced by rural and urban communities. Approaches to Rural and Urban Development.
UNIT-V
Social Work Administration and Social Welfare Administration: Concept, evolution, principles and techniques. Application in the NGOs and State Welfare Agencies.
UNIT – VI
Social Work with the Weaker Sections: Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Castes, Social and Economically Backward Castes, Linguistic and Religious Minorities, Constitutional Provisions, Legislations, Plans and Programmes of the State and Central Government.
Paper-II-OPTIONAL SOCIOLOGY
UNIT I
Basic Sociological Concepts: Society, Community, Culture, Group, Institution, Power and Authority, Social Interaction and processes – Cooperation, Competition, Conflict, Accommodation, Assimilation and Socialization.
UNIT-II
Social Stratification: Meaning and Bases of Marxist, Functionalist, and Weberian perspectives, Social Control and Deviance: Formal and Informal agencies of Social control, Anomie. Social Change: Meaning and Features of Theories and Factors- Evolutionary Theory, Cyclical theory. Marxist Theory: Economic, Technological, Ideological and Cultural factors of Change.
UNIT- III
Indian Social System Unity and Diversity the concept of National Integration, Factors promoting obstacles, Communalism, Casteism, Regionalism and Terrorism. Relevance of Caste and Class in Indian Society the changing dimension of caste, Caste and Politics, Social Change in India – Sanskritization, Westernization, Liberalization and Globalisation, Urbanization and Industrialization. Marriage and Family in India.
UNIT – IV
Social problems and development policy in India: Poverty, Socio-economic Inequality and Exclusion, Problems of the Underprivileged – Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and the Minorities- Constitutional measures for their socio-economic upliftment. Decentralized Planning and Development: Role of Pris and Community Based organizations. Development and Displacement.
UNIT-V
Development: Concepts, Indicators and Approaches, Growth and GDP, Basic basic standard of living Quality of Life, Human Development Index, Gender Development Index, The Capability Approach, The Social Capital Approach, Participative Development and Empowerment, Sustainable Development, Capitalist, Socialist, Gandhian modes of Development.
UNIT-VI
Gender and Society: Culture, Socialization and Gender, Gender Roles. Theories of Gender Relations: Liberal feminism, Radical feminism, Marxist feminism, Ecofeminism. Women and Human Rights. Women labour and the economy in India. Status of Indian Women, status of
Tribal women in Indian society, Violence against Women in India. Gender and Development Approaches-Welfarist and Developmental.
Paper-II – OPTIONAL TRIBAL STUDIES
UNIT -I
Tribal Studies: its development and scope, conceptualizing tribe (Adivasi, Janajati, Banabasi, Girijan, Original people, Indigenous People, Aboriginal, Scheduled Tribe and Mythological terms), Tribal situation in India – Bio- genetic variability, linguistic and socio-economic characteristics of tribal populations and their distribution. Tribal Demography: Distribution of tribal population in India and Odisha, decline of Indigenous population in India. problem of tribal populations in India and Odisha, Demographic Problems of Tribes in Odisha, Tribalization and detribalization.
UNIT- II
Tribal Social Organization: Marriage, Definition and universality, Rules, types, forms and function of marriage, Marriage regulations, Marriage payments. Family: Definition and universality, Family, household and domestic groups; Types of family; Impact of urbanization industrialization on family. Kinship: Definition, Consanguinity and Affinity; Principles and types of Forms of descent groups; Kinship terminology Descent and Alliance. Concepts and Theories of Religion: Religion, Magic and Science, Religious Functionaries, World view, Sacred groves. Impact major Religion on tribal societies.
UNIT – III
Types of Political Organization: State and Stateless Societies, Forms and Agencies of Social Control, Law and Justice: Primitive, Customary and Modern law; Deviation and Social Control; Social Sanction, Feud, Oath and Ordeal, decision making and Punishment.
Tribal Economy: Concepts of Production, Consumption, Exchange and Distribution. Primitive and Peasant Economy, Reciprocity and Redistribution, Types and Technological Levels of Economy: Foraging, Hunting, Pastoralism, Shifting Cultivation, Terrace Cultivation, Dry and Wet Cultivation, Horticulture and Industrial type. Youth dormitory: concept, feature, importance and changing nature. Folk culture and tradition: Art, craft, body, decoration, song, dance, music, games and sports, food and drinks: Socio-Cultural impotence of Tribal Beverages, Dress and ornaments.
Eco-tourism: Meaning and scope, Tribal Museum. Importance of ethnographic museum and preservation of ethnographic specimens.
UNIT- IV
Tribal language and literature of Odisha: Tribal language: classification and distribution. Tribal Scripts: Its origin and development. Ol chiki script (Santal). Soran Sompen script (Saora), Orang Chichi script (Ho) and Grammar. Tribal literature: myth, legends, riddles, proverbs, song tales, aphorisms, oral epics, Oral and documented literature.
UNIT – V
History of administration of tribal areas: Tribal policies, plans, programmes of tribal development and their implementation. 5th and 6th Schedules, Schedule Area and Tribal Area Constitutional provisions and safeguards for Scheduled Tribe. Problems in Tribal Society: Land Alienation, Shifting Cultivation, Housing, Health, Nutrition and Sanitation. Indebtedness, Alcoholism, Bonded Labour, Child Labour, Education, Poverty and Gender Issues. Problems of Displacement and Rehabilitation, Orissa R & R policy 2006.
Tribal Development: Approaches to developments, Role of Anthropology in Tribal and Rural Development, Types of Tribal Movement in India and Odisha. New Panchayati Raj System: PESA Act and Gram Sabha. Role of N.G.Os in Development. Status of Tribal Women, the concept of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups: Concepts, their distribution, special programmes for their development. Contributions of tribal cultures to Indian civilization.
UNIT-VI
Social change and contemporary tribal societies: Impact of modern democratic institutions, development programmes and welfare measures on tribals. The concept of ethnicity: Ethnic conflicts and political developments; Unrest among tribal communities; Regionalism and demand for autonomy; Pseudo-tribalism; Social change among the tribes during pre and post Independent India. Pre-colonial movements: causes and solutions, agrarian unrest in Odisha (Kol rebellion, Kondh Rebellion); Post-colonial movements: causes and solutions (tribal uprising in Mayurbhanj 1948, Kandhamal) Jharkhand movement, Chipko movement
History and Ethnographic Profile of tribes of Odisha: Kandha, Bonda, Soura, Santal, Lodha, Birhor, Mankidia and Hill Kharia.
Paper-II-OPTIONAL ANTHROPOLOGY
UNIT-ITrends and development of Anthropology: Relationships with other disciplines: Social Sciences, Behavioural Sciences, Life Sciences, Medical Sciences, Earth Sciences and Humanities. Main branches of Anthropology, their scope and relevance:
(a) Social cultural Anthropology.
duy
(b) Biological Anthropology. (c) Archaeological Anthropology and
(d) Linguistic Anthropology.
UNIT – IIMan’s place in Animal Kingdom: Primate social behavior; Erect posture and bipedalism, Stages of human evolution: Australopithecine stage, Homoerectus stage, Neanderthal stage (Conservative and progressive variety) Homo – sapien – sapiens stage: (Cro-Magnon Man, Grimaldi Man & Chancelade Man). Theories of organic evolution: Lamarckism, Darwinism and Synthetic theory.
UNIT -IIIHuman Genetics: Mendel’s Law and its application to human population, Human Genome Project. Medical anthropology: socio-cultural and biomedical concept of health, disease and illness; ethno- medicine and medical ecology. Ecological Anthropology: Bio-cultural adaptation to cold, heat and high altitude. Ethical Legal Social Issues (ELSI) in human genetic research
UNIT – IVSocial Organizations: Marriage, Definition and universality: Rules, Types and Function of marriage, and Marriage payments. Family: Definition and universality: Family, household and domestic groups; functions of family, Types of family. Kinship: Consanguinity and Affinity; Principles and types of descent; Kinship terminology; Descent, kinship usages.
Concepts and Theories of Religion, Religion, Magic and Science, Religious Functionaries.
Types of Political Organization, State and Stateless Societies. Forms and Agencies of Social Control, Social Sanction, Law and Justice.
Concepts of Production, consumption, Exchange and Distribution. Primitive and Peasant Economy. Types and Technological Levels Of Economy: Foraging, Hunting, Pastoralism, Shifting Cultivation, Terrace Cultivation, Dry and Wet Cultivation, Horticulture and Industrial.
UNIT-VTheories in Social Anthropology: Neo – Evolutionism, Diffusionism, Structuralism, Structural -Functionalism, Functionalism, Post-Structuralism, Symbolic and Interpretive Anthropology and Postmodern Anthropology.
Role of anthropology in tribal and rural development, characteristics features of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups, their distribution, special programmes for their development. Constitutional safeguards for STs. Contributions of tribal cultures to Indian civilization. Displaced tribes and their socio-economic condition.
UNIT – VIAn outline of Pleistocene epoch, Methods of dating: Relative dating-Stratigraphy, Pollen Analysis, Paleontology; Absolute dating. Radio carbon dating, Potassium-Argon method; Thermoluminescence method: Prehistoric Technology & Tool types of Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic Cultures. Evolution of the Indian Culture and Civilization- Prehistoric Etc.
OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus – Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus?
What is the Exam Pattern for OSSC 2023?
Where can I Get the OSSC Assistant Curator Syllabus PDF?
What are the Total Marks for OSSC Assistant Curator Exam?
How many Questions will be asked in the OSSC Assistant Curator Exam ?